R Interpreter for Apache Zeppelin
Overview
R is a free software environment for statistical computing and graphics.
To run R code and visualize plots in Apache Zeppelin, you will need R on your zeppelin server node (or your dev laptop).
- For Centos:
yum install R R-devel libcurl-devel openssl-devel - For Ubuntu:
apt-get install r-base
Validate your installation with a simple R command:
R -e "print(1+1)"
To enjoy plots, install additional libraries with:
devtools with
R -e "install.packages('devtools', repos = 'http://cran.us.r-project.org')"knitr with
R -e "install.packages('knitr', repos = 'http://cran.us.r-project.org')"ggplot2 with
R -e "install.packages('ggplot2', repos = 'http://cran.us.r-project.org')"Other visualization libraries:
R -e "install.packages(c('devtools','mplot', 'googleVis'), repos = 'http://cran.us.r-project.org'); require(devtools); install_github('ramnathv/rCharts')"
We recommend you to also install the following optional R libraries for happy data analytics:
- glmnet
- pROC
- data.table
- caret
- sqldf
- wordcloud
Supported Interpreters
Zeppelin supports R language in 3 interpreters
| Name | Class | Description |
|---|---|---|
| %r.r | RInterpreter | Vanilla r interpreter, with least dependencies, only R environment and knitr are required.
It is always recommended to use the fully qualified interpreter name %r.r, because %r is ambiguous,
it could mean %spark.r when current note's default interpreter is %spark and %r.r when the default interpreter is %r |
| %r.ir | IRInterpreter | Provide more fancy R runtime via [IRKernel](https://github.com/IRkernel/IRkernel), almost the same experience like using R in Jupyter. It requires more things, but is the recommended interpreter for using R in Zeppelin. |
| %r.shiny | ShinyInterpreter | Run Shiny app in Zeppelin |
If you want to use R with Spark, it is almost the same via %spark.r, %spark.ir & %spark.shiny . You can refer Spark interpreter docs for more details.
Configuration
| Property | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| zeppelin.R.cmd | R | Path of the installed R binary. You should set this property explicitly if R is not in your $PATH(example: /usr/bin/R).
|
| zeppelin.R.knitr | true | Whether to use knitr or not. It is recommended to install [knitr](https://yihui.org/knitr/) |
| zeppelin.R.image.width | 100% | Image width of R plotting |
| zeppelin.R.shiny.iframe_width | 100% | IFrame width of Shiny App |
| zeppelin.R.shiny.iframe_height | 500px | IFrame height of Shiny App |
| zeppelin.R.shiny.portRange | : | Shiny app would launch a web app at some port, this property is to specify the portRange via format 'start':'end', e.g. '5000:5001'. By default it is ':' which means any port. |
| zeppelin.R.maxResult | 1000 | Max number of dataframe rows to display when using z.show |
Play R in Zeppelin docker
For beginner, we would suggest you to play R in Zeppelin docker first. In the Zeppelin docker image, we have already installed R and lots of useful R libraries including IRKernel's prerequisites, so %r.ir is available.
Without any extra configuration, you can run most of tutorial notes under folder R Tutorial directly.
docker run -u $(id -u) -p 8080:8080 -p:6789:6789 --rm --name zeppelin apache/zeppelin:0.11.2
After running the above command, you can open http://localhost:8080 to play R in Zeppelin.
The port 6789 exposed in the above command is for R shiny app. You need to make the following 2 interpreter properties to enable shiny app accessible as iframe in Zeppelin docker container.
zeppelin.R.shiny.portRangeto be6789:6789- Set
ZEPPELIN_LOCAL_IPto be0.0.0.0
Interpreter binding mode
The default interpreter binding mode is globally shared. That means all notes share the same R interpreter.
So we would recommend you to ues isolated per note which means each note has own R interpreter without affecting each other. But it may run out of your machine resource if too many R
interpreters are created. You can run R in yarn mode to avoid this problem.
How to use R Interpreter
There are two different implementations of R interpreters: %r.r and %r.ir.
- Vanilla R Interpreter(
%r.r) behaves like an ordinary REPL and use SparkR to communicate between R process and JVM process. It requiresknitrto be installed. - IRKernel R Interpreter(
%r.ir) behaves like using IRKernel in Jupyter notebook. It is based on jupyter interpreter. Besides jupyter interpreter's prerequisites, IRkernel needs to be installed as well.
Take a look at the tutorial note R Tutorial/1. R Basics for how to write R code in Zeppelin.
R basic expressions
R basic expressions are supported in both %r.r and %r.ir.
R base plotting
R base plotting is supported in both %r.r and %r.ir.
Other plotting
Besides R base plotting, you can use other visualization libraries in both %r.r and %r.ir, e.g. ggplot and googleVis

z.show
z.show() is only available in %r.ir to visualize R dataframe, e.g.
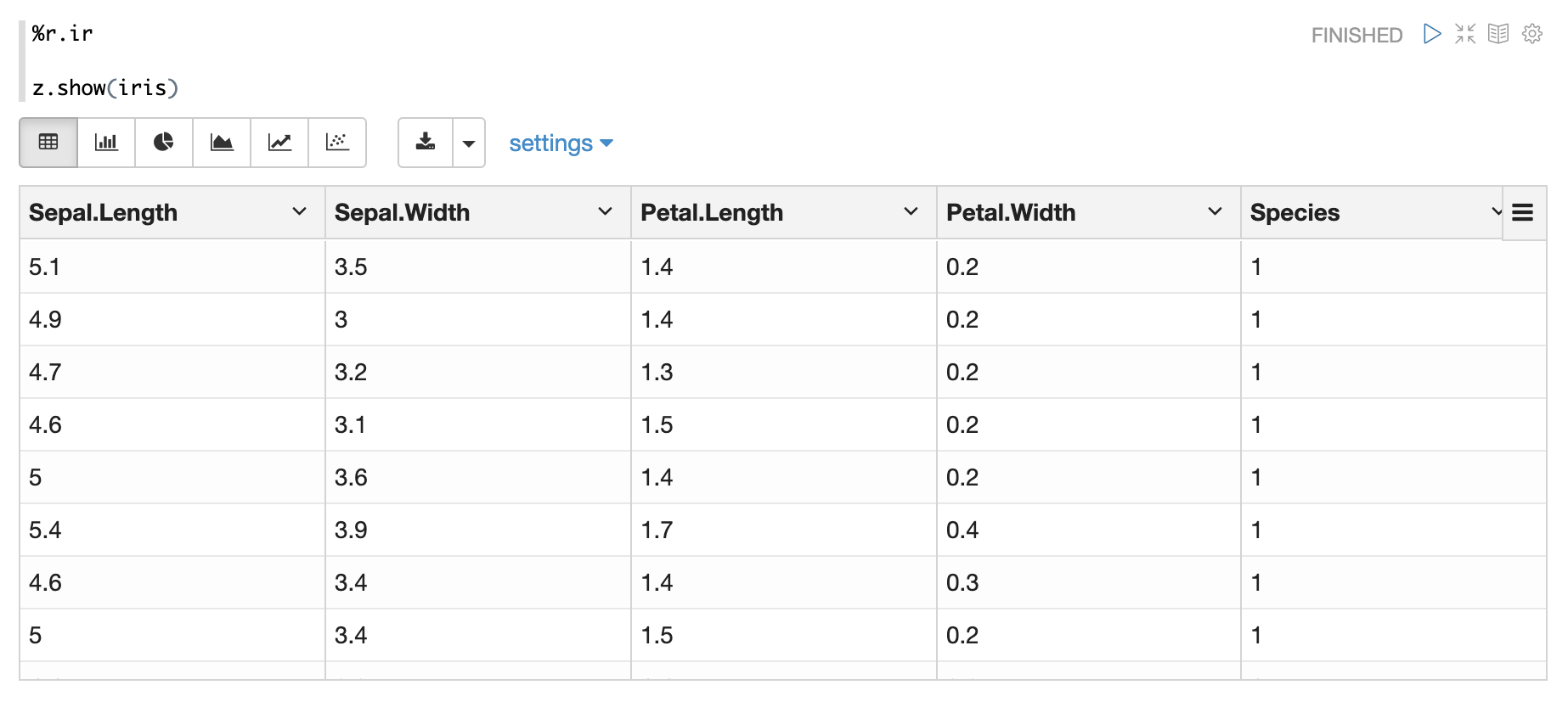
By default, z.show would only display 1000 rows, you can specify the maxRows via z.show(df, maxRows=2000)
Make Shiny App in Zeppelin
Shiny is an R package that makes it easy to build interactive web applications (apps) straight from R.
%r.shiny is used for developing R shiny app in Zeppelin notebook. It only works when IRKernel Interpreter(%r.ir) is enabled.
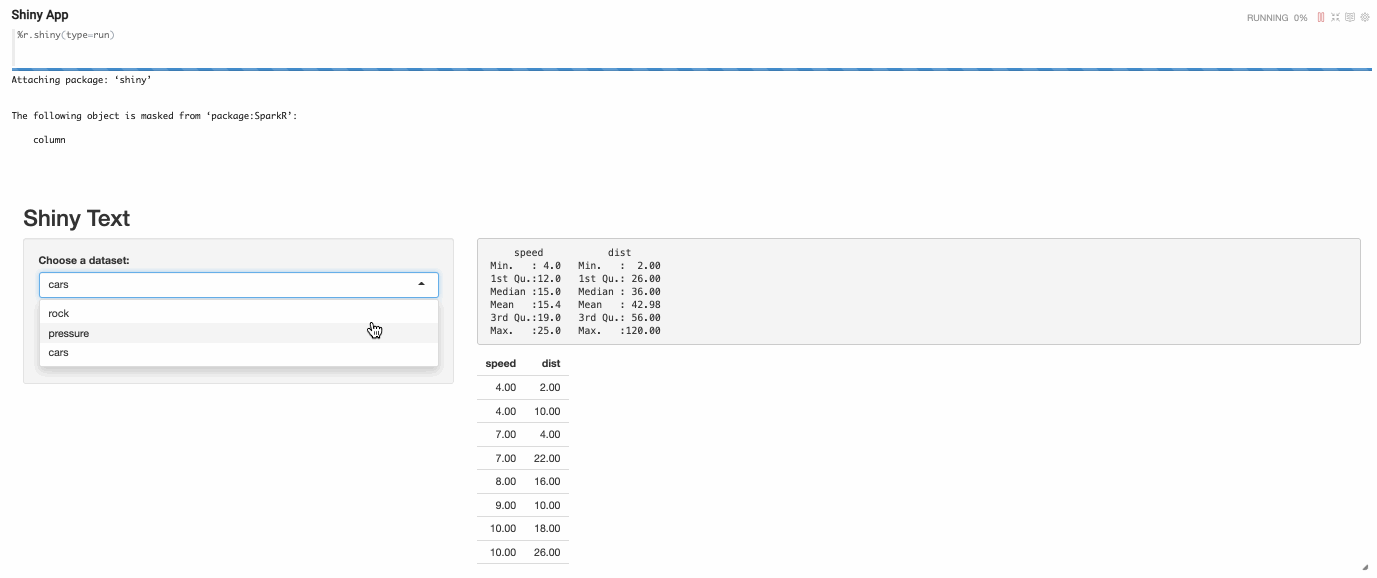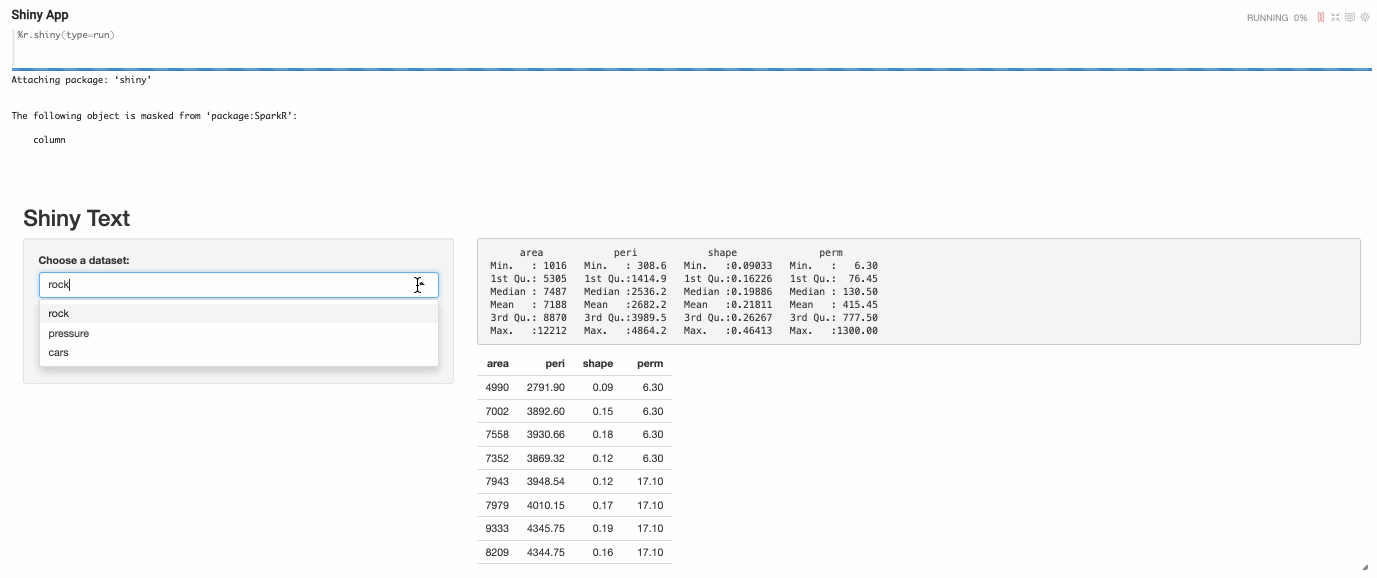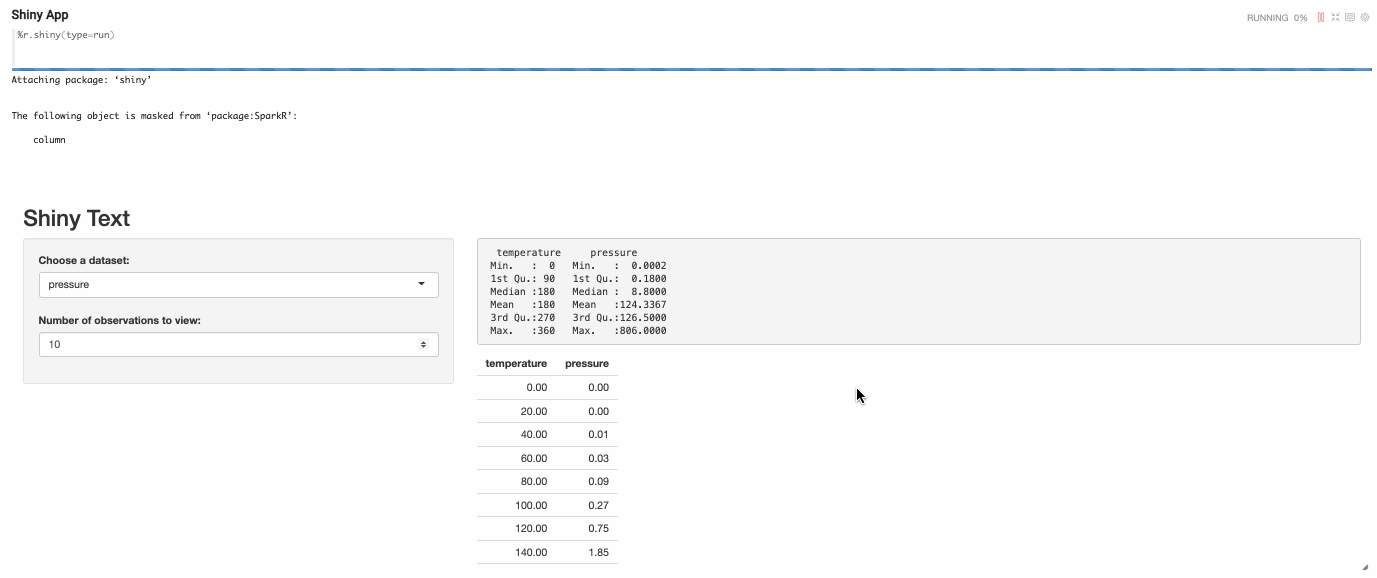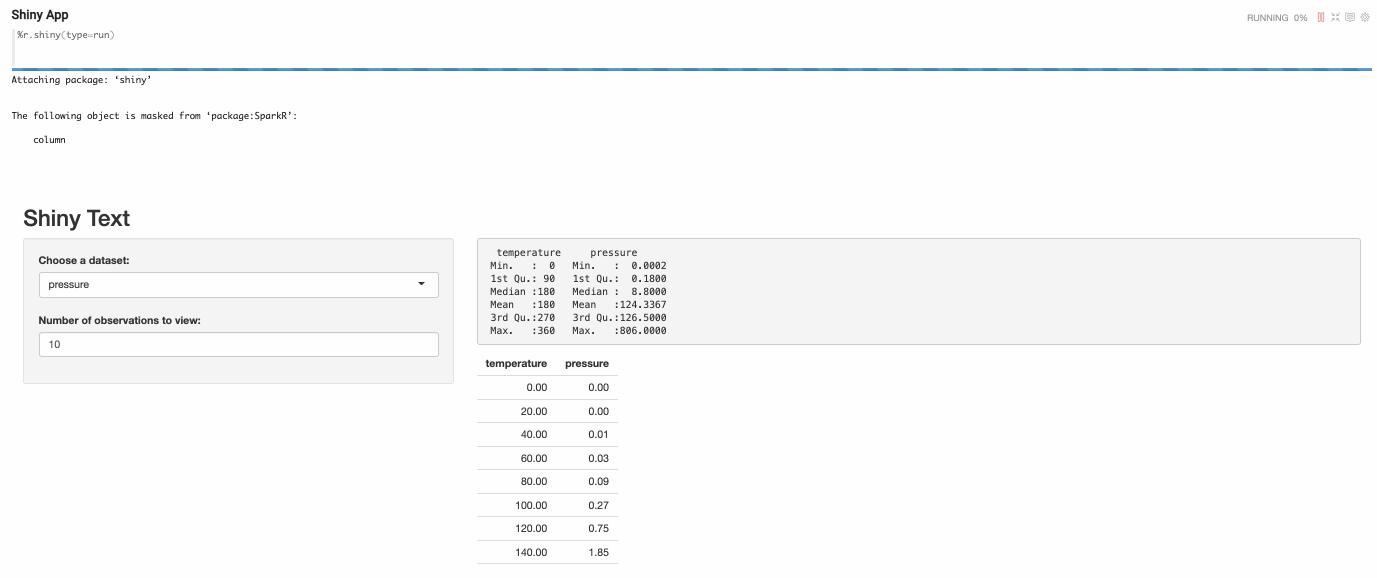
For developing one Shiny App in Zeppelin, you need to write at least 3 paragraphs (server type paragraph, ui type paragraph and run type paragraph)
- Server type R shiny paragraph
%r.shiny(type=server)
# Define server logic to summarize and view selected dataset ----
server <- function(input, output) {
# Return the requested dataset ----
datasetInput <- reactive({
switch(input$dataset,
"rock" = rock,
"pressure" = pressure,
"cars" = cars)
})
# Generate a summary of the dataset ----
output$summary <- renderPrint({
dataset <- datasetInput()
summary(dataset)
})
# Show the first "n" observations ----
output$view <- renderTable({
head(datasetInput(), n = input$obs)
})
}
- UI type R shiny paragraph
%r.shiny(type=ui)
# Define UI for dataset viewer app ----
ui <- fluidPage(
# App title ----
titlePanel("Shiny Text"),
# Sidebar layout with a input and output definitions ----
sidebarLayout(
# Sidebar panel for inputs ----
sidebarPanel(
# Input: Selector for choosing dataset ----
selectInput(inputId = "dataset",
label = "Choose a dataset:",
choices = c("rock", "pressure", "cars")),
# Input: Numeric entry for number of obs to view ----
numericInput(inputId = "obs",
label = "Number of observations to view:",
value = 10)
),
# Main panel for displaying outputs ----
mainPanel(
# Output: Verbatim text for data summary ----
verbatimTextOutput("summary"),
# Output: HTML table with requested number of observations ----
tableOutput("view")
)
)
)
- Run type R shiny paragraph
%r.shiny(type=run)
After executing the run type R shiny paragraph, the shiny app will be launched and embedded as iframe in paragraph.
Take a look at the tutorial note R Tutorial/2. Shiny App for how to develop R shiny app.

Run multiple shiny apps
If you want to run multiple shiny apps, you can specify app in paragraph local property to differentiate different shiny apps.
e.g.
%r.shiny(type=ui, app=app_1)
%r.shiny(type=server, app=app_1)
%r.shiny(type=run, app=app_1)
Run R in yarn cluster
Zeppelin support to run interpreter in yarn cluster. But there's one critical problem to run R in yarn cluster: how to manage the R environment in yarn container. Because yarn cluster is a distributed cluster which is composed of many nodes, and your R interpreter can start in any node. It is not practical to manage R environment in each node.
So in order to run R in yarn cluster, we would suggest you to use conda to manage your R environment, and Zeppelin can ship your R conda environment to yarn container, so that each R interpreter can have its own R environment without affecting each other.
To be noticed, you can only run IRKernel interpreter(%r.ir) in yarn cluster. So make sure you include at least the following prerequisites in the below conda env:
- python
- jupyter
- grpcio
- protobuf
- r-base
- r-essentials
- r-irkernel
python, jupyter, grpcio and protobuf are required for jupyter interpreter, because IRKernel interpreter is based on jupyter interpreter. Others are for R runtime.
Following are instructions of how to run R in yarn cluster. You can find all the code in the tutorial note R Tutorial/3. R Conda Env in Yarn Mode.
Step 1
We would suggest you to use conda pack to create archive of conda environment.
Here's one example of yaml file which is used to generate a conda environment with R and some useful R libraries.
- Create a yaml file for conda environment, write the following content into file
r_env.yml
name: r_env
channels:
- conda-forge
- defaults
dependencies:
- python=3.9
- jupyter
- grpcio
- protobuf
- r-base=3
- r-essentials
- r-evaluate
- r-base64enc
- r-knitr
- r-ggplot2
- r-irkernel
- r-shiny
- r-googlevis
- Create conda environment via this yaml file using either
condaormamba
conda env create -f r_env.yml
mamba env create -f r_env.yml
- Pack the conda environment using
conda
conda pack -n r_env
Step 2
Specify the following properties to enable yarn mode for R interpreter via inline configuration
%r.conf
zeppelin.interpreter.launcher yarn
zeppelin.yarn.dist.archives hdfs:///tmp/r_env.tar.gz#environment
zeppelin.interpreter.conda.env.name environment
zeppelin.yarn.dist.archives is the R conda environment tar file which is created in step 1. This tar will be shipped to yarn container and untar in the working directory of yarn container.
hdfs:///tmp/r_env.tar.gz is the R conda archive file you created in step 2. environment in hdfs:///tmp/r_env.tar.gz#environment is the folder name after untar.
This folder name should be the same as zeppelin.interpreter.conda.env.name.
Step 3
Now you can use run R interpreter in yarn container and also use any R libraries you specify in step 1.
