Generic JDBC Interpreter for Apache Zeppelin
Overview
JDBC interpreter lets you create a JDBC connection to any data sources seamlessly.
Inserts, Updates, and Upserts are applied immediately after running each statement.
By now, it has been tested with:

If you are using other databases not in the above list, please feel free to share your use case. It would be helpful to improve the functionality of JDBC interpreter.
Create a new JDBC Interpreter
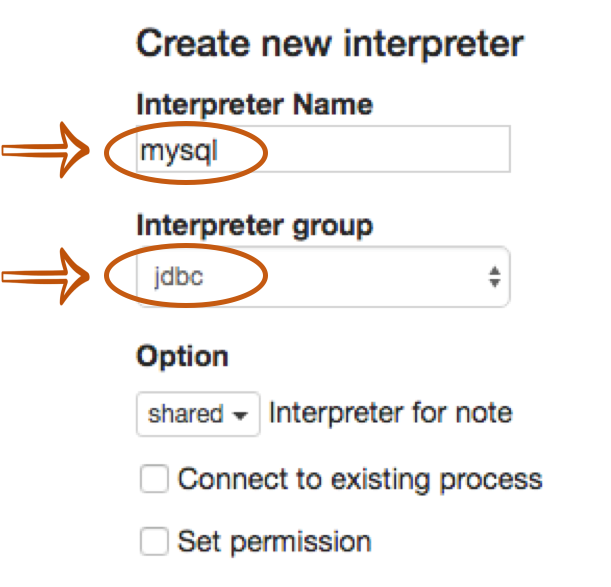
First, click + Create button at the top-right corner in the interpreter setting page.

Fill Interpreter name field with whatever you want to use as the alias(e.g. mysql, mysql2, hive, redshift, and etc..).
Please note that this alias will be used as %interpreter_name to call the interpreter in the paragraph.
Then select jdbc as an Interpreter group.
The default driver of JDBC interpreter is set as PostgreSQL. It means Zeppelin includes PostgreSQL driver jar in itself.
So you don't need to add any dependencies(e.g. the artifact name or path for PostgreSQL driver jar) for PostgreSQL connection.
The JDBC interpreter properties are defined by default like below.
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| common.max_count | 1000 | The maximun number of SQL result to display |
| default.driver | org.postgresql.Driver | JDBC Driver Name |
| default.password | The JDBC user password | |
| default.url | jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/ | The URL for JDBC |
| default.user | gpadmin | The JDBC user name |
| default.precode | Some SQL which executes every time after initialization of the interpreter (see Binding mode) | |
| default.statementPrecode | SQL code which executed before the SQL from paragraph, in the same database session (database connection) | |
| default.completer.schemaFilters | Сomma separated schema (schema = catalog = database) filters to get metadata for completions. Supports '%' symbol is equivalent to any set of characters. (ex. prod_v_%,public%,info) | |
| default.completer.ttlInSeconds | 120 | Time to live sql completer in seconds (-1 to update everytime, 0 to disable update) |
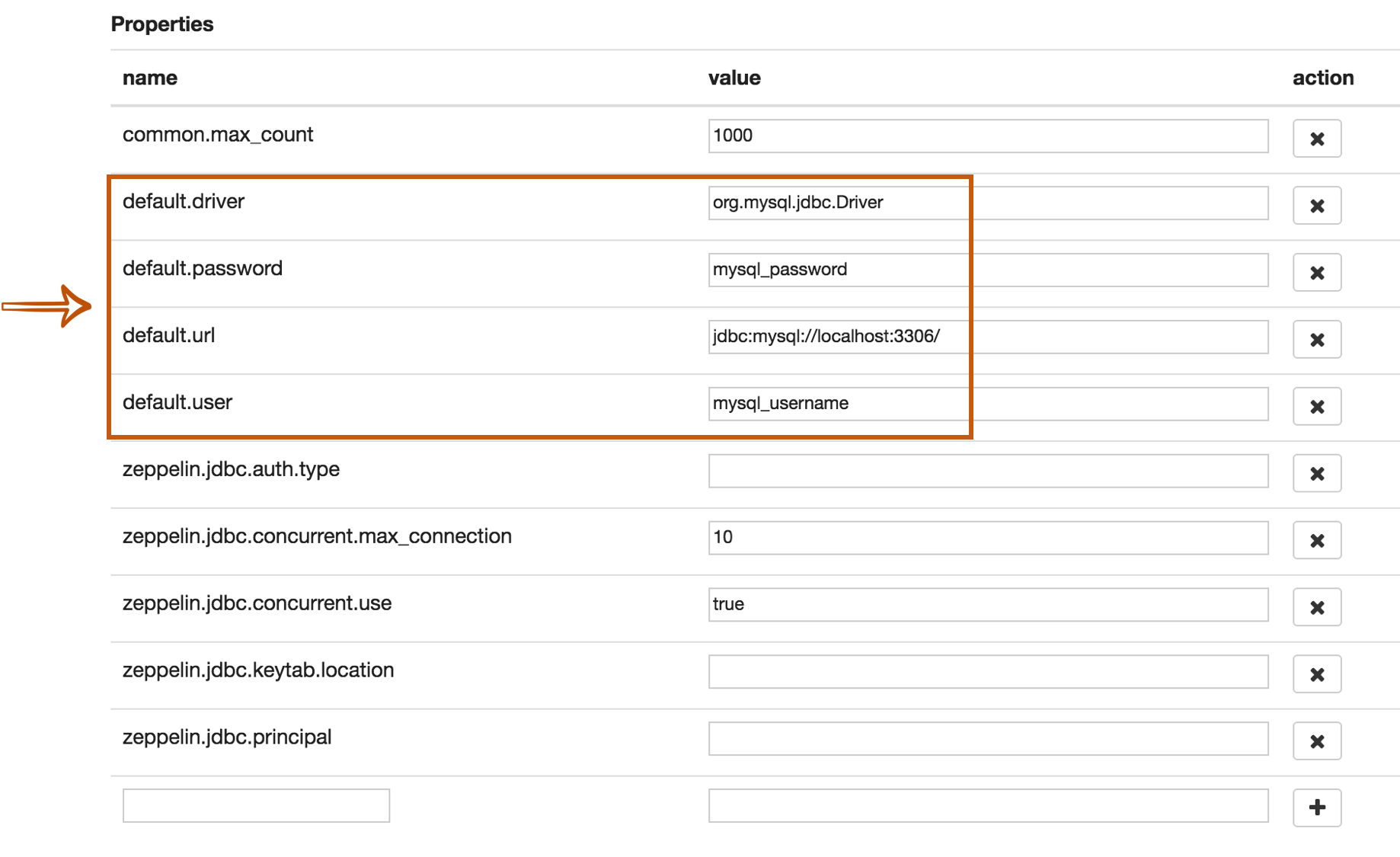
If you want to connect other databases such as Mysql, Redshift and Hive, you need to edit the property values.
You can also use Credential for JDBC authentication.
If default.user and default.password properties are deleted(using X button) for database connection in the interpreter setting page,
the JDBC interpreter will get the account information from Credential.
The below example is for Mysql connection.
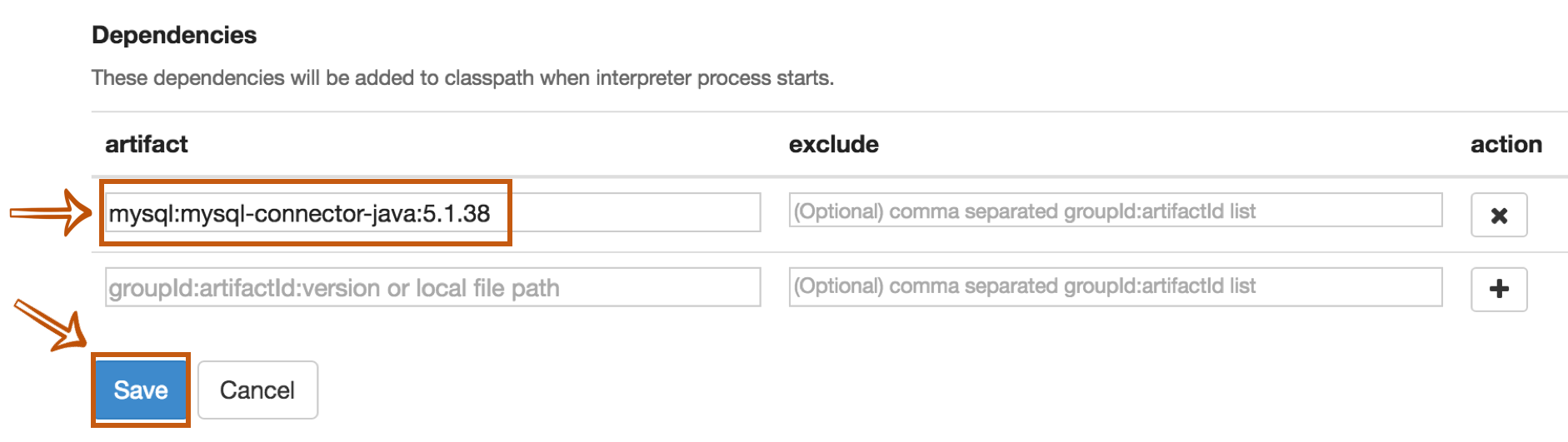
The last step is Dependency Setting. Since Zeppelin only includes PostgreSQL driver jar by default, you need to add each driver's maven coordinates or JDBC driver's jar file path for the other databases.
That's it. You can find more JDBC connection setting examples(Mysql, MariaDB, Redshift, Apache Hive, Presto/Trino, Impala, Apache Phoenix, and Apache Tajo) in this section.
JDBC Interpreter Datasource Pool Configuration
The Jdbc interpreter uses the connection pool technology, and supports users to do some personal configuration of the connection pool. For example, we can configure default.validationQuery='select 1' and default.testOnBorrow=true in the Interpreter configuration to avoid the "Invalid SessionHandle" runtime error caused by Session timeout when connecting to HiveServer2 through JDBC interpreter.
The Jdbc Interpreter supports the following database connection pool configurations:
| Property Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| testOnBorrow | false | The indication of whether objects will be validated before being borrowed from the pool. If the object fails to validate, it will be dropped from the pool, and we will attempt to borrow another. |
| testOnCreate | false | The indication of whether objects will be validated after creation. If the object fails to validate, the borrow attempt that triggered the object creation will fail. |
| testOnReturn | false | The indication of whether objects will be validated before being returned to the pool. |
| testWhileIdle | false | The indication of whether objects will be validated by the idle object evictor (if any). If an object fails to validate, it will be dropped from the pool. |
| timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis | -1L | The number of milliseconds to sleep between runs of the idle object evictor thread. When non-positive, no idle object evictor thread will be run. |
| maxWaitMillis | -1L | The maximum number of milliseconds that the pool will wait (when there are no available connections) for a connection to be returned before throwing an exception, or -1 to wait indefinitely. |
| maxIdle | 8 | The maximum number of connections that can remain idle in the pool, without extra ones being released, or negative for no limit. |
| minIdle | 0 | The minimum number of connections that can remain idle in the pool, without extra ones being created, or zero to create none. |
| maxTotal | -1 | The maximum number of active connections that can be allocated from this pool at the same time, or negative for no limit. |
| validationQuery | show database | The SQL query that will be used to validate connections from this pool before returning them to the caller. If specified, this query MUST be an SQL SELECT statement that returns at least one row. If not specified, connections will be validation by calling the isValid() method. |
More properties
There are more JDBC interpreter properties you can specify like below.
| Property Name | Description |
|---|---|
| common.max_result | Max number of SQL result to display to prevent the browser overload. This is common properties for all connections |
| zeppelin.jdbc.auth.type | Types of authentications' methods supported are SIMPLE, and KERBEROS |
| zeppelin.jdbc.principal | The principal name to load from the keytab |
| zeppelin.jdbc.keytab.location | The path to the keytab file |
| zeppelin.jdbc.auth.kerberos.proxy.enable | When auth type is Kerberos, enable/disable Kerberos proxy with the login user to get the connection. Default value is true. |
| default.jceks.file | jceks store path (e.g: jceks://file/tmp/zeppelin.jceks) |
| default.jceks.credentialKey | jceks credential key |
| zeppelin.jdbc.interpolation | Enables ZeppelinContext variable interpolation into paragraph text. Default value is false. |
| zeppelin.jdbc.maxConnLifetime | Maximum of connection lifetime in milliseconds. A value of zero or less means the connection has an infinite lifetime. |
You can also add more properties by using this method. For example, if a connection needs a schema parameter, it would have to add the property as follows:
| name | value |
|---|---|
| default.schema | schema_name |
How to use
Run the paragraph with JDBC interpreter
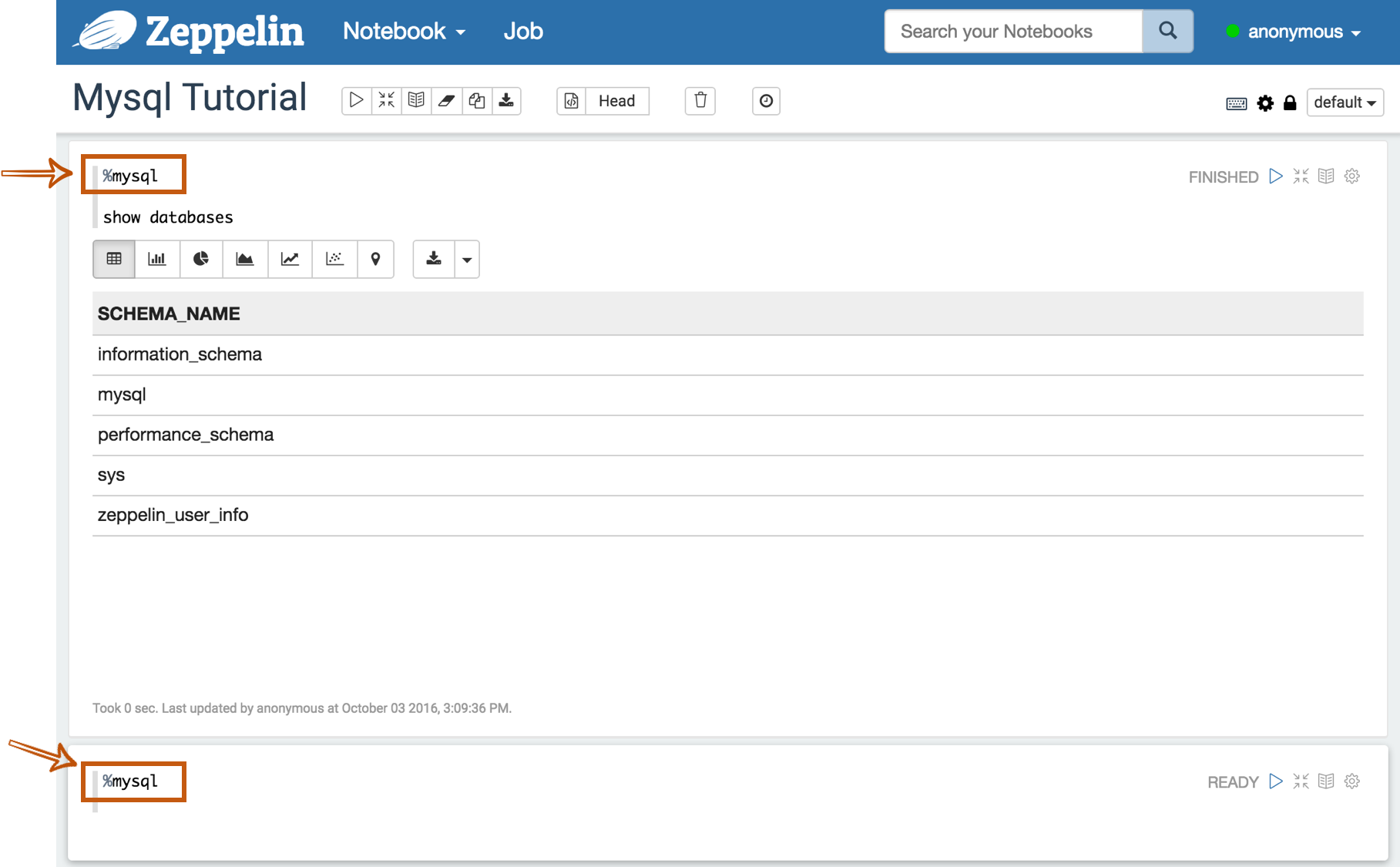
To test whether your databases and Zeppelin are successfully connected or not, type %jdbc_interpreter_name(e.g. %mysql) at the top of the paragraph and run show databases.
%jdbc_interpreter_name
show databases
If the paragraph is FINISHED without any errors, a new paragraph will be automatically added after the previous one with %jdbc_interpreter_name.
So you don't need to type this prefix in every paragraphs' header.
Multiple SQL statements
You can write multiple sql statements in one paragraph, just separate them with semi-colon. e.g
%jdbc_interpreter_name
USE zeppelin_demo;
CREATE TABLE pet (name VARCHAR(20), owner VARCHAR(20),
species VARCHAR(20), sex CHAR(1), birth DATE, death DATE);
SQL Comment
2 kinds of SQL comments are supported:
- Single line comment start with
-- - Multiple line comment around with
/* ... */
%jdbc_interpreter_name
-- single line comment
show tables;
/* multiple
line
comment
*/
select * from test_1;
Apply Zeppelin Dynamic Forms
You can leverage Zeppelin Dynamic Form inside your queries. You can use both the text input and select form parametrization features.
Run SQL Continuously
By default, sql statements in one paragraph are executed only once. But you can run it continuously by specifying local property refreshInterval (unit: milli-seconds),
So that the sql statements are executed every interval of refreshInterval milli-seconds. This is useful when your data in database is updated continuously by external system,
and you can build dynamic dashboard in Zeppelin via this approach.
e.g. Here we query the mysql which is updated continuously by other external system.
Usage precode
You can set precode for each data source. Code runs once while opening the connection.
Properties
An example settings of interpreter for the two data sources, each of which has its precode parameter.
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
| default.driver | org.postgresql.Driver |
| default.password | 1 |
| default.url | jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/ |
| default.user | postgres |
| default.precode | set search_path='test_path' |
| default.driver | com.mysql.jdbc.Driver |
| default.password | 1 |
| default.url | jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ |
| default.user | root |
| default.precode | set @v=12 |
Usage
Test of execution precode for each data source.
%jdbc
show search_path
Returns value of search_path which is set in the default jdbc (use postgresql) interpreter's default.precode.
%mysql
select @v
Returns value of v which is set in the mysql interpreter's default.precode.
Examples
Here are some examples you can refer to. Including the below connectors, you can connect every databases as long as it can be configured with it's JDBC driver.
Postgres
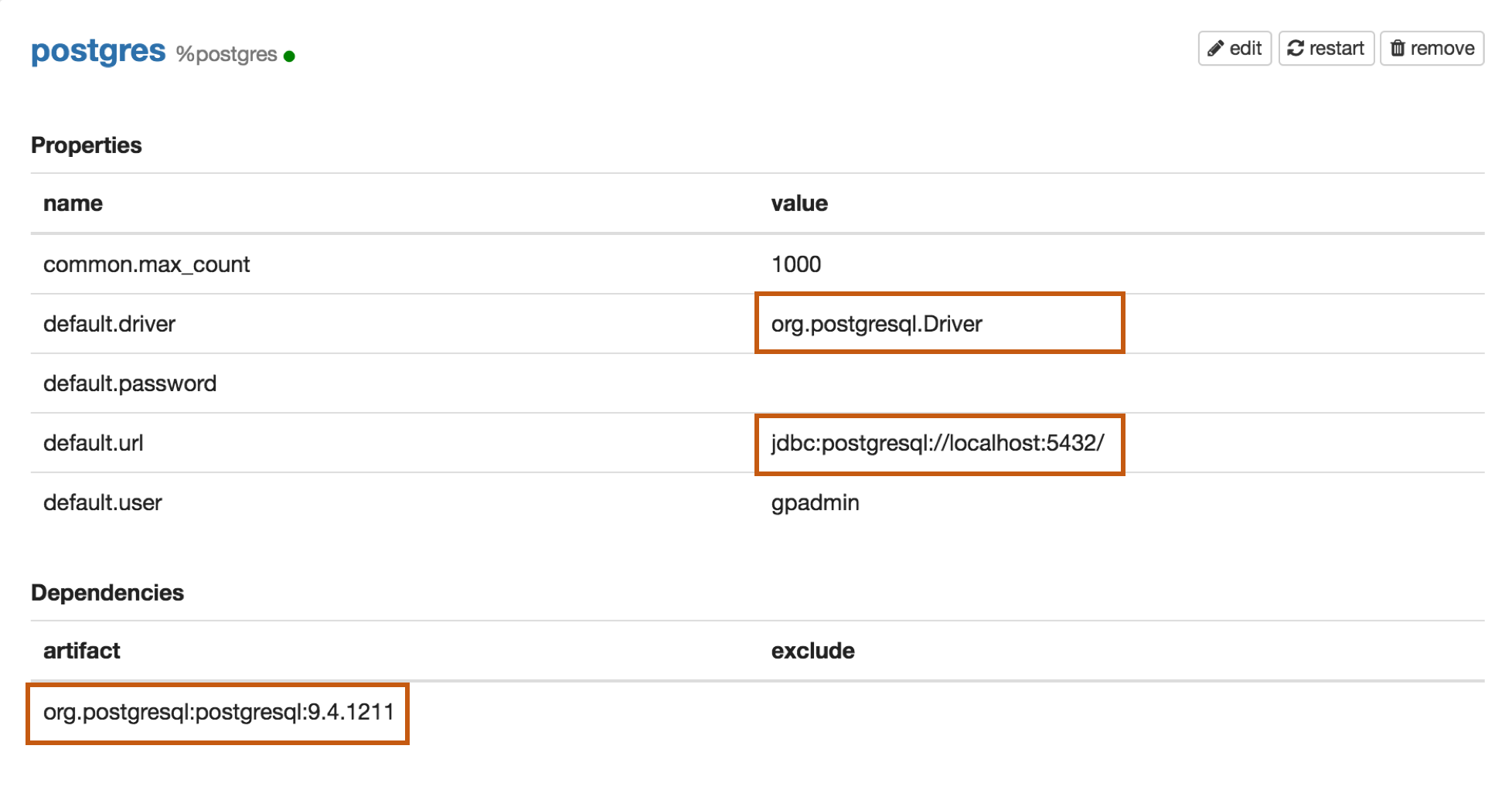
Properties
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| default.driver | org.postgresql.Driver |
| default.url | jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/ |
| default.user | mysql_user |
| default.password | mysql_password |
Dependencies
| Artifact | Excludes |
|---|---|
| org.postgresql:postgresql:9.4.1211 |
Maven Repository: org.postgresql:postgresql
Mysql
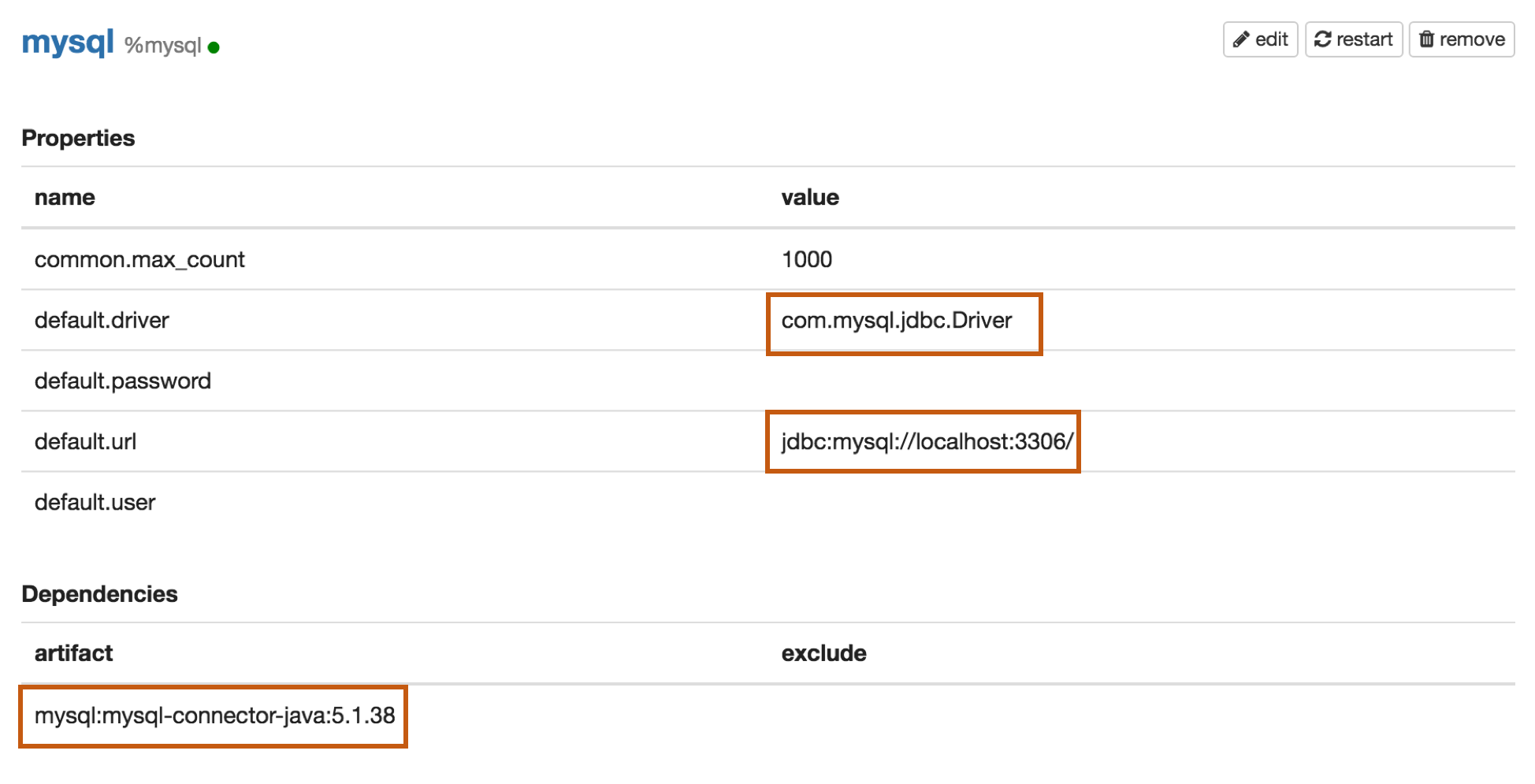
Properties
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| default.driver | com.mysql.jdbc.Driver |
| default.url | jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ |
| default.user | mysql_user |
| default.password | mysql_password |
Dependencies
| Artifact | Excludes |
|---|---|
| mysql:mysql-connector-java:5.1.38 |
Maven Repository: mysql:mysql-connector-java
MariaDB

Properties
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| default.driver | org.mariadb.jdbc.Driver |
| default.url | jdbc:mariadb://localhost:3306 |
| default.user | mariadb_user |
| default.password | mariadb_password |
Dependencies
| Artifact | Excludes |
|---|---|
| org.mariadb.jdbc:mariadb-java-client:1.5.4 |
Maven Repository: org.mariadb.jdbc:mariadb-java-client
Redshift

Properties
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| default.driver | com.amazon.redshift.jdbc42.Driver |
| default.url | jdbc:redshift://your-redshift-instance-address.redshift.amazonaws.com:5439/your-database |
| default.user | redshift_user |
| default.password | redshift_password |
Dependencies
| Artifact | Excludes |
|---|---|
| com.amazonaws:aws-java-sdk-redshift:1.11.51 |
Maven Repository: com.amazonaws:aws-java-sdk-redshift
Apache Hive
Zeppelin just connect to hiveserver2 to run hive sql via hive jdbc. There are 2 cases of connecting with Hive:
- Connect to Hive without KERBEROS
- Connect to Hive with KERBEROS
Each case requires different settings.
Connect to Hive without KERBEROS
In this scenario, you need to make the following settings at least. By default, hive job run as user of default.user.
Refer impersonation if you want hive job run as the Zeppelin login user when authentication is enabled.
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| default.driver | org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver |
| default.url | jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000 |
| default.user | hive_user |
| Artifact | Excludes |
|---|---|
| org.apache.hive:hive-jdbc:2.3.4 |
Connect to Hive with KERBEROS
In this scenario, you need to make the following settings at least. By default, hive job run as user of client principal (zeppelin.jdbc.principal).
Refer impersonation if you want hive job run as the Zeppelin login user when authentication is enabled.
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| default.driver | org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver |
| default.url | jdbc:hive2://emr-header-1:10000/default;principal={hive_server2_principal} |
| zeppelin.jdbc.auth.type | KERBEROS |
| zeppelin.jdbc.keytab.location | keytab of client |
| zeppelin.jdbc.principal | principal of client |
| Artifact | Excludes |
|---|---|
| org.apache.hive:hive-jdbc:2.3.4 | |
| org.apache.hive:hive-exec:2.3.4 |
Maven Repository : org.apache.hive:hive-jdbc
Impersonation
When Zeppelin server is running with authentication enabled, then the interpreter can utilize Hive's user proxy feature i.e. send extra parameter for creating and running a session ("hive.server2.proxy.user=": "${loggedInUser}"). This is particularly useful when multiple users are sharing a notebook.
To enable this set following:
default.proxy.user.propertyashive.server2.proxy.user
See User Impersonation in interpreter for more information.
Sample configuration
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| hive.driver | org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver |
| hive.url | jdbc:hive2://hive-server-host:2181/;serviceDiscoveryMode=zooKeeper;zooKeeperNamespace=hiveserver2 |
| hive.proxy.user.property | hive.server2.proxy.user |
| zeppelin.jdbc.auth.type | SIMPLE |
Presto/Trino
Properties
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| default.driver | io.prestosql.jdbc.PrestoDriver |
| default.url | jdbc:presto://presto-server:9090/hive |
| default.user | presto_user |
Trino JDBC Driver Docs
Presto JDBC Driver Docs
Dependencies
| Artifact | Excludes |
|---|---|
| io.prestosql:presto-jdbc:350 |
Impala
Properties
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| default.driver | org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver |
| default.url | jdbc:hive2://emr-header-1.cluster-47080:21050/;auth=noSasl |
Dependencies
| Artifact | Excludes |
|---|---|
| org.apache.hive:hive-jdbc:2.3.4 |
Dependencies
| Artifact | Excludes |
|---|---|
| io.prestosql:presto-jdbc:350 |
Apache Phoenix
Phoenix supports thick and thin connection types:
- Thick client is faster, but must connect directly to ZooKeeper and HBase RegionServers.
- Thin client has fewer dependencies and connects through a Phoenix Query Server instance.
Use the appropriate default.driver, default.url, and the dependency artifact for your connection type.
Thick client connection
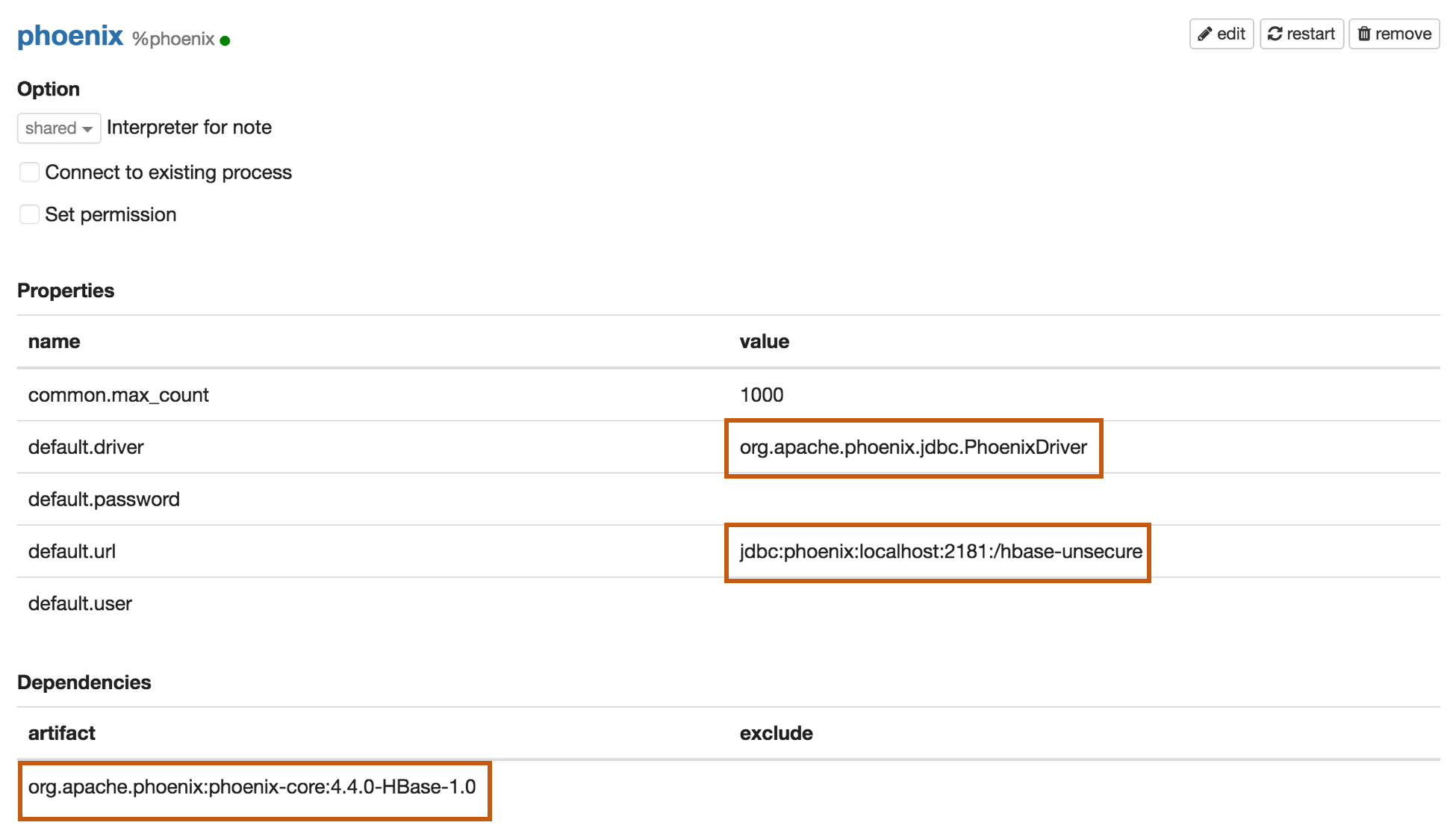
Properties
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| default.driver | org.apache.phoenix.jdbc.PhoenixDriver |
| default.url | jdbc:phoenix:localhost:2181:/hbase-unsecure |
| default.user | phoenix_user |
| default.password | phoenix_password |
Dependencies
| Artifact | Excludes |
|---|---|
| org.apache.phoenix:phoenix-core:4.4.0-HBase-1.0 |
Maven Repository: org.apache.phoenix:phoenix-core
Thin client connection

Properties
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| default.driver | org.apache.phoenix.queryserver.client.Driver |
| default.url | jdbc:phoenix:thin:url=http://localhost:8765;serialization=PROTOBUF |
| default.user | phoenix_user |
| default.password | phoenix_password |
Dependencies
Before Adding one of the below dependencies, check the Phoenix version first.
| Artifact | Excludes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| org.apache.phoenix:phoenix-server-client:4.7.0-HBase-1.1 | For Phoenix 4.7 |
|
| org.apache.phoenix:phoenix-queryserver-client:4.8.0-HBase-1.2 | For Phoenix 4.8+ |
Maven Repository: org.apache.phoenix:phoenix-queryserver-client
Apache Tajo
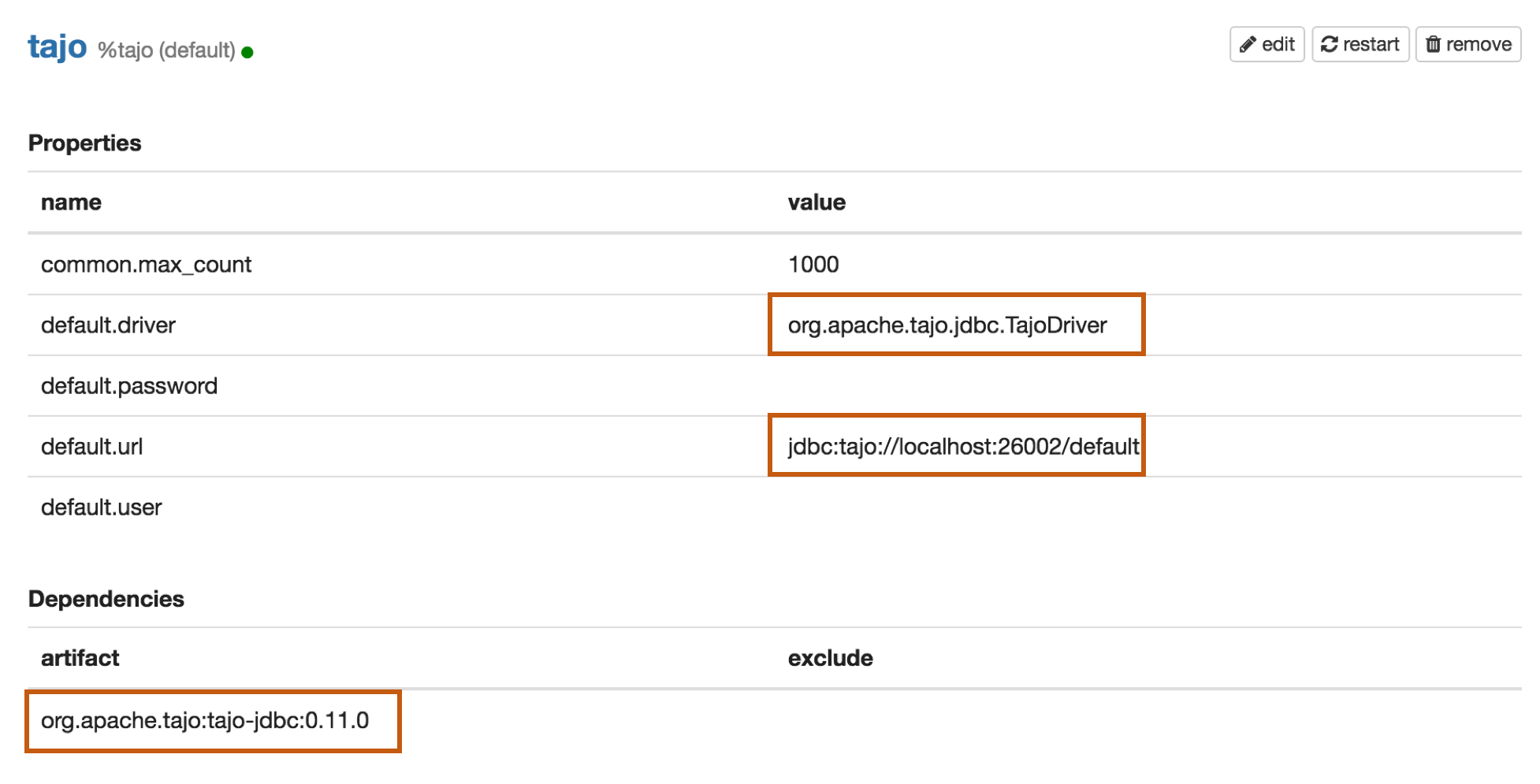
Properties
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| default.driver | org.apache.tajo.jdbc.TajoDriver |
| default.url | jdbc:tajo://localhost:26002/default |
Dependencies
| Artifact | Excludes |
|---|---|
| org.apache.tajo:tajo-jdbc:0.11.0 |
Maven Repository: org.apache.tajo:tajo-jdbc
Object Interpolation
The JDBC interpreter also supports interpolation of ZeppelinContext objects into the paragraph text.
The following example shows one use of this facility:
In Scala cell:
z.put("country_code", "KR")
// ...
In later JDBC cell:
%jdbc_interpreter_name
select * from patents_list where
priority_country = '{country_code}' and filing_date like '2015-%'
Object interpolation is disabled by default, and can be enabled for all instances of the JDBC interpreter by
setting the value of the property zeppelin.jdbc.interpolation to true (see More Properties above).
More details of this feature can be found in the Spark interpreter documentation under
Zeppelin-Context
Bug reporting
If you find a bug using JDBC interpreter, please create a JIRA ticket.
