Spark Interpreter for Apache Zeppelin
Overview
Apache Spark is a fast and general-purpose cluster computing system. It provides high-level APIs in Java, Scala, Python and R, and an optimized engine that supports general execution graphs. Apache Spark is supported in Zeppelin with Spark interpreter group which consists of following interpreters.
| Name | Class | Description |
|---|---|---|
| %spark | SparkInterpreter | Creates a SparkContext/SparkSession and provides a Scala environment |
| %spark.pyspark | PySparkInterpreter | Provides a Python environment |
| %spark.ipyspark | IPySparkInterpreter | Provides a IPython environment |
| %spark.r | SparkRInterpreter | Provides an vanilla R environment with SparkR support |
| %spark.ir | SparkIRInterpreter | Provides an R environment with SparkR support based on Jupyter IRKernel |
| %spark.shiny | SparkShinyInterpreter | Used to create R shiny app with SparkR support |
| %spark.sql | SparkSQLInterpreter | Provides a SQL environment |
Main Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Support multiple versions of Spark | You can run different versions of Spark in one Zeppelin instance |
| Support multiple versions of Scala | You can run different Scala versions (2.12/2.13) of Spark in on Zeppelin instance |
| Support multiple languages | Scala, SQL, Python, R are supported, besides that you can also collaborate across languages, e.g. you can write Scala UDF and use it in PySpark |
| Support multiple execution modes | Local | Standalone | Yarn | K8s |
| Interactive development | Interactive development user experience increase your productivity |
| Inline Visualization | You can visualize Spark Dataset/DataFrame vis Python/R's plotting libraries, and even you can make SparkR Shiny app in Zeppelin | Multi-tenancy | Multiple user can work in one Zeppelin instance without affecting each other. | Rest API Support | You can not only submit Spark job via Zeppelin notebook UI, but also can do that via its rest api (You can use Zeppelin as Spark job server). |
Play Spark in Zeppelin docker
For beginner, we would suggest you to play Spark in Zeppelin docker.
In the Zeppelin docker image, we have already installed
miniconda and lots of useful python and R libraries
including IPython and IRkernel prerequisites, so %spark.pyspark would use IPython and %spark.ir is enabled.
Without any extra configuration, you can run most of tutorial notes under folder Spark Tutorial directly.
First you need to download Spark, because there's no Spark binary distribution shipped with Zeppelin.
e.g. Here we download Spark 3.1.2 to/mnt/disk1/spark-3.1.2,
and we mount it to Zeppelin docker container and run the following command to start Zeppelin docker container.
docker run -u $(id -u) -p 8080:8080 -p 4040:4040 --rm -v /mnt/disk1/spark-3.1.2:/opt/spark -e SPARK_HOME=/opt/spark --name zeppelin apache/zeppelin:0.11.1
After running the above command, you can open http://localhost:8080 to play Spark in Zeppelin. We only verify the spark local mode in Zeppelin docker, other modes may not work due to network issues.
-p 4040:4040 is to expose Spark web ui, so that you can access Spark web ui via http://localhost:8081.
Configuration
The Spark interpreter can be configured with properties provided by Zeppelin. You can also set other Spark properties which are not listed in the table. For a list of additional properties, refer to Spark Available Properties.
| Property | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
SPARK_HOME |
Location of spark distribution | |
| spark.master | local[*] | Spark master uri. e.g. spark://masterhost:7077 |
| spark.submit.deployMode | The deploy mode of Spark driver program, either "client" or "cluster", Which means to launch driver program locally ("client") or remotely ("cluster") on one of the nodes inside the cluster. | |
| spark.app.name | Zeppelin | The name of spark application. |
| spark.driver.cores | 1 | Number of cores to use for the driver process, only in cluster mode. |
| spark.driver.memory | 1g | Amount of memory to use for the driver process, i.e. where SparkContext is initialized, in the same format as JVM memory strings with a size unit suffix ("k", "m", "g" or "t") (e.g. 512m, 2g). |
| spark.executor.cores | 1 | The number of cores to use on each executor |
| spark.executor.memory | 1g | Executor memory per worker instance. e.g. 512m, 32g |
| spark.executor.instances | 2 | The number of executors for static allocation |
| spark.files | Comma-separated list of files to be placed in the working directory of each executor. Globs are allowed. | |
| spark.jars | Comma-separated list of jars to include on the driver and executor classpaths. Globs are allowed. | |
| spark.jars.packages | Comma-separated list of Maven coordinates of jars to include on the driver and executor classpaths. The coordinates should be groupId:artifactId:version. If spark.jars.ivySettings is given artifacts will be resolved according to the configuration in the file, otherwise artifacts will be searched for in the local maven repo, then maven central and finally any additional remote repositories given by the command-line option --repositories. | |
PYSPARK_PYTHON |
python | Python binary executable to use for PySpark in both driver and executors (default is python).
Property spark.pyspark.python take precedence if it is set |
PYSPARK_DRIVER_PYTHON |
python | Python binary executable to use for PySpark in driver only (default is PYSPARK_PYTHON).
Property spark.pyspark.driver.python take precedence if it is set |
| zeppelin.pyspark.useIPython | false | Whether use IPython when the ipython prerequisites are met in %spark.pyspark |
| zeppelin.R.cmd | R | R binary executable path. |
| zeppelin.spark.concurrentSQL | false | Execute multiple SQL concurrently if set true. |
| zeppelin.spark.concurrentSQL.max | 10 | Max number of SQL concurrently executed |
| zeppelin.spark.maxResult | 1000 | Max number rows of Spark SQL result to display. |
| zeppelin.spark.run.asLoginUser | true | Whether run spark job as the zeppelin login user, it is only applied when running spark job in hadoop yarn cluster and shiro is enabled. |
| zeppelin.spark.printREPLOutput | true | Print scala REPL output |
| zeppelin.spark.useHiveContext | true | Use HiveContext instead of SQLContext if it is true. Enable hive for SparkSession |
| zeppelin.spark.enableSupportedVersionCheck | true | Do not change - developer only setting, not for production use |
| zeppelin.spark.sql.interpolation | false | Enable ZeppelinContext variable interpolation into spark sql |
| zeppelin.spark.uiWebUrl | Overrides Spark UI default URL. Value should be a full URL (ex: http://{hostName}/{uniquePath}. In Kubernetes mode, value can be Jinja template string with 3 template variables PORT, SERVICENAME and SERVICEDOMAIN . (e.g.: http://{{PORT}}-{{SERVICENAME}}.{{SERVICEDOMAIN}} ). In yarn mode, value could be a knox url with {{applicationId}} as placeholder, (e.g.: https://knox-server:8443/gateway/yarnui/yarn/proxy/{{applicationId}}/) | |
| spark.webui.yarn.useProxy | false | whether use yarn proxy url as Spark weburl, e.g. http://localhost:8088/proxy/application1583396598068_0004 |
Without any configuration, Spark interpreter works out of box in local mode. But if you want to connect to your Spark cluster, you'll need to follow below two simple steps.
- Set SPARK_HOME
- Set master
Set SPARK_HOME
There are several options for setting SPARK_HOME.
- Set
SPARK_HOMEinzeppelin-env.sh - Set
SPARK_HOMEin interpreter setting page - Set
SPARK_HOMEvia inline generic configuration
Set SPARK_HOME in zeppelin-env.sh
If you work with only one version of Spark, then you can set SPARK_HOME in zeppelin-env.sh because any setting in zeppelin-env.sh is globally applied.
e.g.
export SPARK_HOME=/usr/lib/spark
You can optionally set more environment variables in zeppelin-env.sh
# set hadoop conf dir
export HADOOP_CONF_DIR=/usr/lib/hadoop
Set SPARK_HOME in interpreter setting page
If you want to use multiple versions of Spark, then you need to create multiple Spark interpreters and set SPARK_HOME separately. e.g.
Create a new Spark interpreter spark33 for Spark 3.3 and set its SPARK_HOME in interpreter setting page,
Create a new Spark interpreter spark34 for Spark 3.4 and set its SPARK_HOME in interpreter setting page.
Set SPARK_HOME via inline generic configuration
Besides setting SPARK_HOME in interpreter setting page, you can also use inline generic configuration to put the
configuration with code together for more flexibility. e.g.

Set master
After setting SPARK_HOME, you need to set spark.master property in either interpreter setting page or inline configuartion. The value may vary depending on your Spark cluster deployment type.
For example,
- local[*] in local mode
- spark://master:7077 in standalone cluster
- yarn-client in Yarn client mode (Not supported in Spark 3.x, refer below for how to configure yarn-client in Spark 3.x)
- yarn-cluster in Yarn cluster mode (Not supported in Spark 3.x, refer below for how to configure yarn-cluster in Spark 3.x)
- mesos://host:5050 in Mesos cluster
That's it. Zeppelin will work with any version of Spark and any deployment type without rebuilding Zeppelin in this way. For the further information about Spark & Zeppelin version compatibility, please refer to "Available Interpreters" section in Zeppelin download page.
Note that without setting SPARK_HOME, it's running in local mode with included version of Spark. The included version may vary depending on the build profile. And this included version Spark has limited function, so it
is always recommended to set SPARK_HOME.
Yarn client mode and local mode will run driver in the same machine with zeppelin server, this would be dangerous for production. Because it may run out of memory when there's many Spark interpreters running at the same time. So we suggest you
only allow yarn-cluster mode via setting zeppelin.spark.only_yarn_cluster in zeppelin-site.xml.
Configure yarn mode for Spark 3.x
Specifying yarn-client & yarn-cluster in spark.master is not supported in Spark 3.x any more, instead you need to use spark.master and spark.submit.deployMode together.
| Mode | spark.master | spark.submit.deployMode |
|---|---|---|
| Yarn Client | yarn | client |
| Yarn Cluster | yarn | cluster |
Interpreter binding mode
The default interpreter binding mode is globally shared. That means all notes share the same Spark interpreter.
So we recommend you to use isolated per note which means each note has own Spark interpreter without affecting each other. But it may run out of your machine resource if too many
Spark interpreters are created, so we recommend to always use yarn-cluster mode in production if you run Spark in hadoop cluster. And you can use inline configuration via %spark.conf in the first paragraph to customize your spark configuration.
You can also choose scoped mode. For scoped per note mode, Zeppelin creates separated scala compiler/python shell for each note but share a single SparkContext/SqlContext/SparkSession.
SparkContext, SQLContext, SparkSession, ZeppelinContext
SparkContext, SQLContext, SparkSession (for spark 2.x, 3.x) and ZeppelinContext are automatically created and exposed as variable names sc, sqlContext, spark and z respectively, in Scala, Python and R environments.
Note that Scala/Python/R environment shares the same SparkContext, SQLContext, SparkSession and ZeppelinContext instance.
Yarn Mode
Zeppelin support both yarn client and yarn cluster mode (yarn cluster mode is supported from 0.8.0). For yarn mode, you must specify SPARK_HOME & HADOOP_CONF_DIR.
Usually you only have one hadoop cluster, so you can set HADOOP_CONF_DIR in zeppelin-env.sh which is applied to all Spark interpreters. If you want to use spark against multiple hadoop cluster, then you need to define
HADOOP_CONF_DIR in interpreter setting or via inline generic configuration.
K8s Mode
Regarding how to run Spark on K8s in Zeppelin, please check this doc.
PySpark
There are 2 ways to use PySpark in Zeppelin:
- Vanilla PySpark
- IPySpark
Vanilla PySpark (Not Recommended)
Vanilla PySpark interpreter is almost the same as vanilla Python interpreter except Spark interpreter inject SparkContext, SQLContext, SparkSession via variables sc, sqlContext, spark.
By default, Zeppelin would use IPython in %spark.pyspark when IPython is available (Zeppelin would check whether ipython's prerequisites are met), Otherwise it would fall back to the vanilla PySpark implementation.
IPySpark (Recommended)
You can use IPySpark explicitly via %spark.ipyspark. IPySpark interpreter is almost the same as IPython interpreter except Spark interpreter inject SparkContext, SQLContext, SparkSession via variables sc, sqlContext, spark.
For the IPython features, you can refer doc Python Interpreter
SparkR
Zeppelin support SparkR via %spark.r, %spark.ir and %spark.shiny. Here's configuration for SparkR Interpreter.
| Spark Property | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| zeppelin.R.cmd | R | R binary executable path. |
| zeppelin.R.knitr | true | Whether use knitr or not. (It is recommended to install knitr and use it in Zeppelin) |
| zeppelin.R.image.width | 100% | R plotting image width. |
| zeppelin.R.render.options | out.format = 'html', comment = NA, echo = FALSE, results = 'asis', message = F, warning = F, fig.retina = 2 | R plotting options. |
| zeppelin.R.shiny.iframe_width | 100% | IFrame width of Shiny App |
| zeppelin.R.shiny.iframe_height | 500px | IFrame height of Shiny App |
| zeppelin.R.shiny.portRange | : | Shiny app would launch a web app at some port, this property is to specify the portRange via format ' |
Refer R doc for how to use R in Zeppelin.
SparkSql
Spark sql interpreter share the same SparkContext/SparkSession with other Spark interpreters. That means any table registered in scala, python or r code can be accessed by Spark sql. For examples:
%spark
case class People(name: String, age: Int)
var df = spark.createDataFrame(List(People("jeff", 23), People("andy", 20)))
df.createOrReplaceTempView("people")
%spark.sql
select * from people
You can write multiple sql statements in one paragraph. Each sql statement is separated by semicolon. Sql statement in one paragraph would run sequentially. But sql statements in different paragraphs can run concurrently by the following configuration.
- Set
zeppelin.spark.concurrentSQLto true to enable the sql concurrent feature, underneath zeppelin will change to use fairscheduler for Spark. And also setzeppelin.spark.concurrentSQL.maxto control the max number of sql statements running concurrently. - Configure pools by creating
fairscheduler.xmlunder yourSPARK_CONF_DIR, check the official spark doc Configuring Pool Properties Set pool property via setting paragraph local property. e.g.
%spark(pool=pool1) sql statement
This pool feature is also available for all versions of scala Spark, PySpark. For SparkR, it is only available starting from 2.3.0.
Dependency Management
For Spark interpreter, it is not recommended to use Zeppelin's Dependency Management for managing
third party dependencies (%spark.dep is removed from Zeppelin 0.9 as well). Instead, you should set the standard Spark properties as following:
| Spark Property | Spark Submit Argument | Description |
|---|---|---|
| spark.files | --files | Comma-separated list of files to be placed in the working directory of each executor. Globs are allowed. |
| spark.jars | --jars | Comma-separated list of jars to include on the driver and executor classpaths. Globs are allowed. |
| spark.jars.packages | --packages | Comma-separated list of Maven coordinates of jars to include on the driver and executor classpaths. The coordinates should be groupId:artifactId:version. If spark.jars.ivySettings is given artifacts will be resolved according to the configuration in the file, otherwise artifacts will be searched for in the local maven repo, then maven central and finally any additional remote repositories given by the command-line option --repositories. |
As general Spark properties, you can set them in via inline configuration or interpreter setting page or in zeppelin-env.sh via environment variable SPARK_SUBMIT_OPTIONS.
For examples:
export SPARK_SUBMIT_OPTIONS="--files <my_file> --jars <my_jar> --packages <my_package>"
To be noticed, SPARK_SUBMIT_OPTIONS is deprecated and will be removed in future release.
ZeppelinContext
Zeppelin automatically injects ZeppelinContext as variable z in your Scala/Python environment. ZeppelinContext provides some additional functions and utilities.
See Zeppelin-Context for more details. For Spark interpreter, you can use z to display Spark Dataset/Dataframe.

Setting up Zeppelin with Kerberos
Logical setup with Zeppelin, Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC), and Spark on YARN:
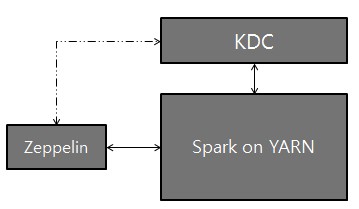
There are several ways to make Spark work with kerberos enabled hadoop cluster in Zeppelin.
Share one single hadoop cluster. In this case you just need to specify
zeppelin.server.kerberos.keytabandzeppelin.server.kerberos.principalin zeppelin-site.xml, Spark interpreter will use these setting by default.Work with multiple hadoop clusters. In this case you can specify
spark.yarn.keytabandspark.yarn.principalto overridezeppelin.server.kerberos.keytabandzeppelin.server.kerberos.principal.
Configuration Setup
On the server that Zeppelin is installed, install Kerberos client modules and configuration, krb5.conf. This is to make the server communicate with KDC.
Add the two properties below to Spark configuration (
[SPARK_HOME]/conf/spark-defaults.conf):spark.yarn.principal spark.yarn.keytab
NOTE: If you do not have permission to access for the above spark-defaults.conf file, optionally, you can add the above lines to the Spark Interpreter setting through the Interpreter tab in the Zeppelin UI.
- That's it. Play with Zeppelin!
User Impersonation
In yarn mode, the user who launch the zeppelin server will be used to launch the Spark yarn application. This is not a good practise. Most of time, you will enable shiro in Zeppelin and would like to use the login user to submit the Spark yarn app. For this purpose, you need to enable user impersonation for more security control. In order the enable user impersonation, you need to do the following steps
Step 1 Enable user impersonation setting hadoop's core-site.xml. E.g. if you are using user zeppelin to launch Zeppelin, then add the following to core-site.xml, then restart both hdfs and yarn.
<property>
<name>hadoop.proxyuser.zeppelin.groups</name>
<value>*</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hadoop.proxyuser.zeppelin.hosts</name>
<value>*</value>
</property>
Step 2 Enable interpreter user impersonation in Spark interpreter's interpreter setting. (Enable shiro first of course)
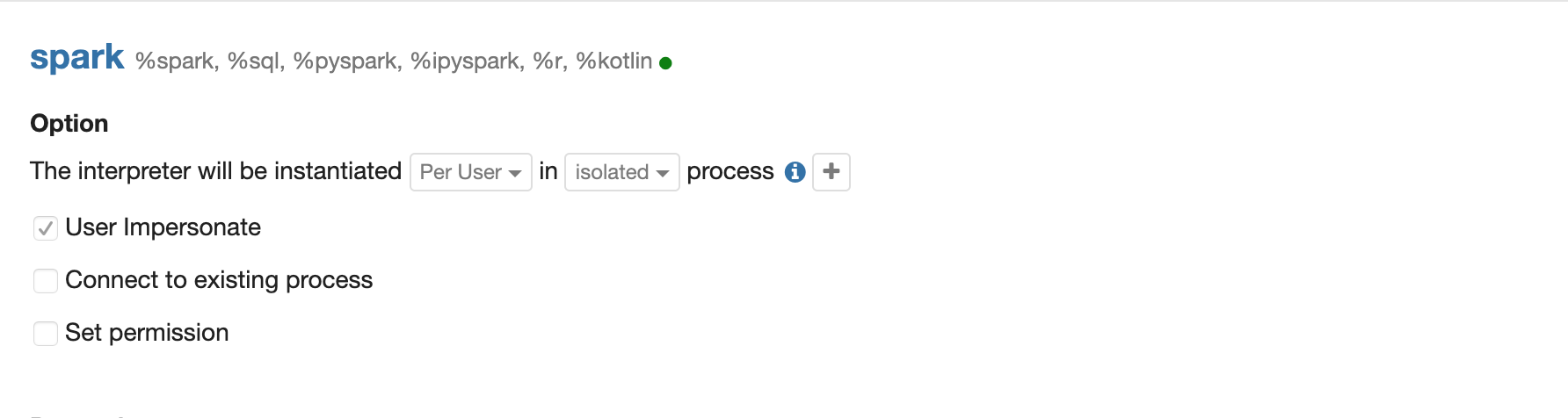
Step 3(Optional) If you are using kerberos cluster, then you need to set zeppelin.server.kerberos.keytab and zeppelin.server.kerberos.principal to the user(aka. user in Step 1) you want to
impersonate in zeppelin-site.xml.
Community
Join our community to discuss with others.
